Do you have the latest version? We’ll show you how to check what version of Android you have, what the latest version offers, how to update, and what’s next for Android.
The Latest Android Version is Android 12
At the time of writing, the latest version of the Android OS is 12, released on October 4, 2021. Of course, unless you’re running a “stock” Android device, you may not have access to Android 12 for quite some time. This is because each device manufacturer tends to develop and put their own custom “skin” on top of Android. For example, Samsung Galaxy phones have One UI, Xiaomi has MIUI, OnePlus has OxygenOS, and so on, which causes the delay.
Key Features of Android 12
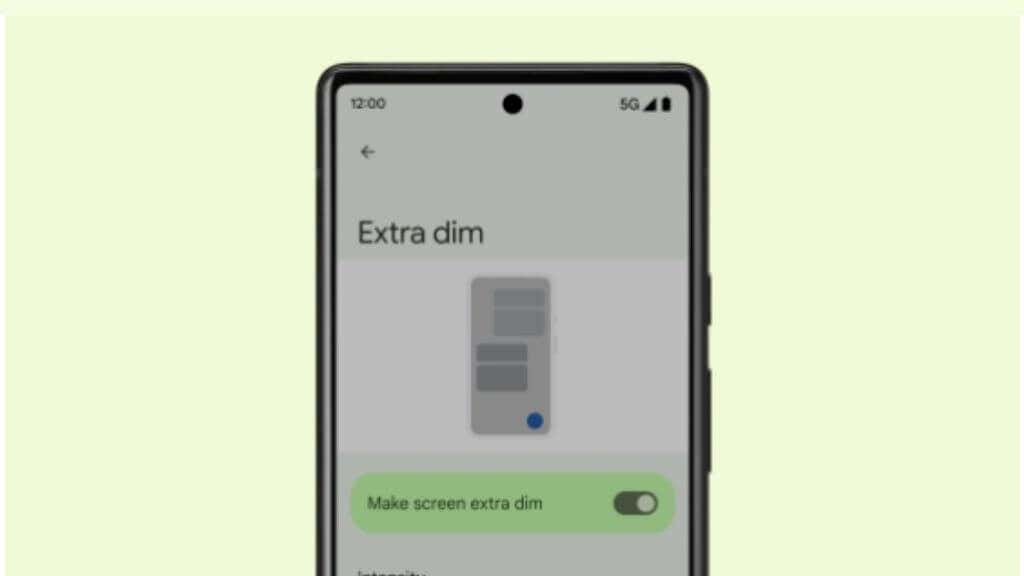
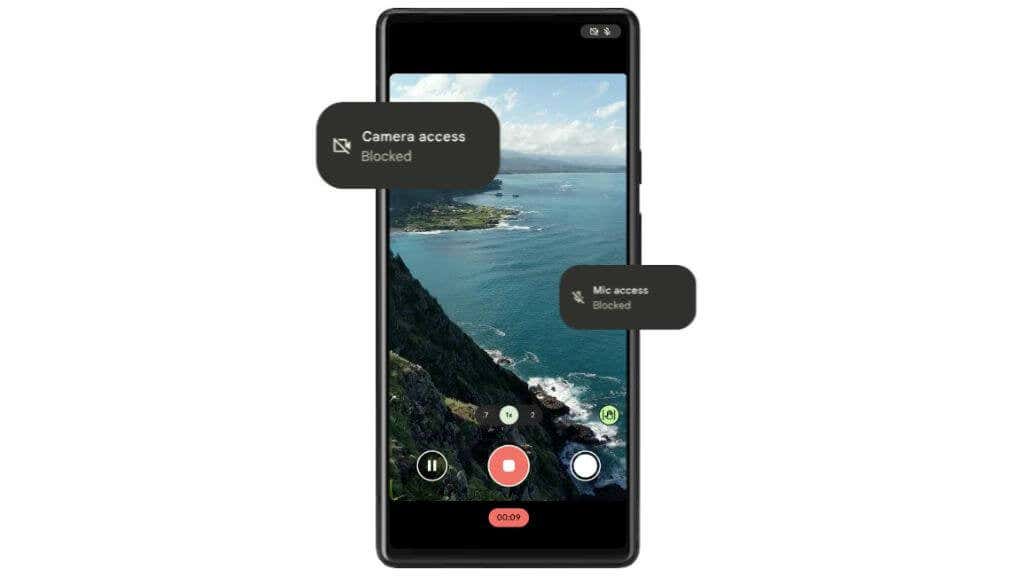
Like all major versions of Android, Android 12 comes with several key features that will either convince you to update or stick with the Android version that you know and love. Android 12 is a major refinement of the operating system. The graphical interface has received a major facelift. System colors can automatically adjust based on your wallpaper. Widgets have a new look, animations and motions have been modernized. Everything on the home screen feels more polished and premium. On-screen elements are more spaced out, and Android 12 takes better advantage of the high-resolution screens that modern phones have. You can also take screenshots that extend beyond the actual screen limits, such as an entire web page as you scroll through it using the scrollable screenshot feature. Another notable set of features in Android 12 relates to accessibility. There’s a new window magnifier, an extra dim mode for those with light sensitivity or who want to browse in the dark. Depending on your vision needs, you can also bold text across the entire phone and do system-wide color tweaking, including switching the phone to grayscale. Privacy features bring Android 12 more in line with the latest version of Apple’s iOS. There are new clear indicators when your mic or camera is recording, and you can permanently disable your camera and mic if you don’t want any apps to access them.
What Happened to the Dessert Names?
Although the first Android versions didn’t have code names, you may remember that for a long time, each Android version was known by dessert names:
Cupcake (Android 1.5) Donut (Android 1.6) Eclair (Android 2.0 – 2.1) Froyo (Android 2.2 – 2.2.3) Gingerbread (Android 2.3 – 2.3.7) Honeycomb (Android 3.0 – 3.2.6) Ice Cream Sandwich (Android 4.0 – 4.0.4) Jelly Bean (Android 4.1- 4.3.1) KitKat (Android 4.4 – 4.4.4) Lollipop (Android 5.0 – 5.1.1) Marshmallow (Android 6.0 – 6.0.1) Nougat (Android 7.0 – 7.1.2) Oreo (Android 8.0 – 8.1) Pie (Android 9.0)
With Android 10 (aka “Quince Tart”), Google decided that it would switch over to version numbers just like Apple’s iOS. The dessert code names haven’t gone away, but they are no longer the official public name of the operating system. For example, Android 11’s internal codename is “Red Velvet Cake.” Android 12’s dessert name is “Snow Cone”!
How to Update to the Latest Version of Android
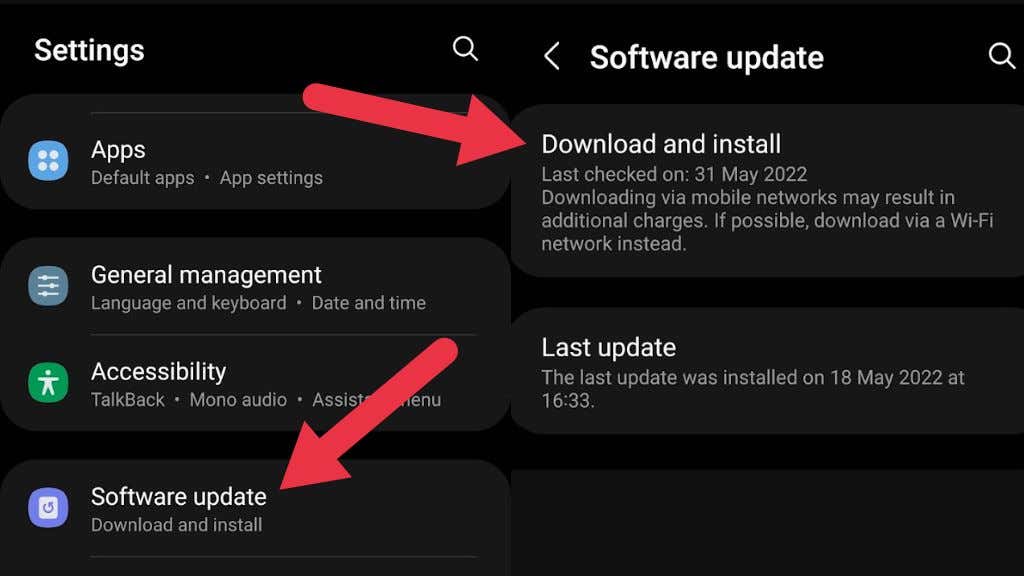
If you’re raring to go and want to upgrade to the latest version of Android, there are a few ways to do it. The one that requires the least effort is simply waiting until you receive a notification that your phone is ready for a system update. Then you can simply schedule the update or proceed with it immediately, downloading the update over Wi-Fi. If you want to check whether an update is available manually, open Settings and select software update. On older versions of Android, you may have to go to Settings > System > System Update or “About This Device” or something similar.
Why Can’t I Update to the Latest Version of Android?
You may have been excited to see the official release date for the new version of Android has come and gone, but the offer to upgrade to it doesn’t seem to be available. As mentioned above, most Android phone makers take the time to customize Android before releasing it on their phones. This can take a few months, so you may have to wait for those new features. Then again, companies like Samsung or Xiaomi add features to their custom version of Android that isn’t in the stock Android release or will only come in a future version. For example, a screen recording feature was only added to Android 11, but Samsung Galaxy phones (among others) have had this for years before Android 11’s release. If your handset is older than two years, you may never receive the option to update your phone. Android phones have a notoriously short support cycle compared to iPhones, and you may find that you’re left out in the cold as they turn their attention to new handsets. This is changing; for example, Samsung has committed to at least four Android version updates for its Galaxy S22 phone range. If you have a stock Android device such as the Google Pixel 6 or other Pixel phones, you can update as soon as a new Android version drops. However, Android may not support older models because they can’t handle new functionality.
What Happens if You Don’t Update?
If you can’t (or don’t want to) update to a newer version of Android, you can keep using your phone as usual. You should still get security updates and bug fixes for a few years. However, you may find that Android apps from the Google Play Store eventually drop support for your Android version, making your phone less useful over time.
When is Android 13 Available?
While Google has not given a firm release date for Android 13 “Tiramisu”, general expectations are that it will have a stable release late in Q3 or early in Q4 of 2022. The next Google I/O event will likely provide a firm date. Except for stock Android devices, users can expect to get Android 13 sometime in 2023.
Previewing Upcoming Android Versions
If you don’t want to wait to experience the next version of Android, you can try the preview builds meant for developers. If you have a Google Pixel device, you can install a developer preview build using developer tools on your phone. However, we don’t recommend that anyone do this on their primary device. You can also grab a preview build from Google’s Developer site and run it in an Android Emulator to get a taste of what’s to come.
Getting New Android Versions on Unsupported Devices
If your phone manufacturer has abandoned Android updates for your device, you always have the option of installing a custom ROM on your phone. This means erasing the factory system image and replacing it with one made by a third party. This is an excellent way to update a phone or tablet that is no longer receiving updates but may have competent hardware to run new versions of Android. However, you may face some downsides, such as losing manufacturer-specific features for that device. For example, if you have a fancy foldable phone, it’s unlikely that a custom ROM not meant for that handset would support folding functions. Flashing your phone with a custom ROM is not for the faint-hearted, but if you follow the steps to root your device, install custom recovery software, and finally flash a custom ROM, you should get through it.
I Want to Go Back to an Older Version of Android
Getting the latest version of Android is great, but sometimes you may feel like you prefer the way things used to be, or perhaps there are significant bugs on your phone that you can’t live with until a patch arrives. It is possible to roll back to a previous version of Android, but not using official methods. Instead, check out our guide on downgrading to an older Android version.